Manage your Kubernetes deployments
This guide demonstrates how to bring your Kubernetes deployment management experience into Port. You will learn how to:
- Ingest Kubernetes cluster, deployment, and pod data into Port's software catalog using Port's Kubernetes integration.
- Set up self-service actions to manage Kubernetes deployments and pods (restart deployment and delete pod).
Common use cases
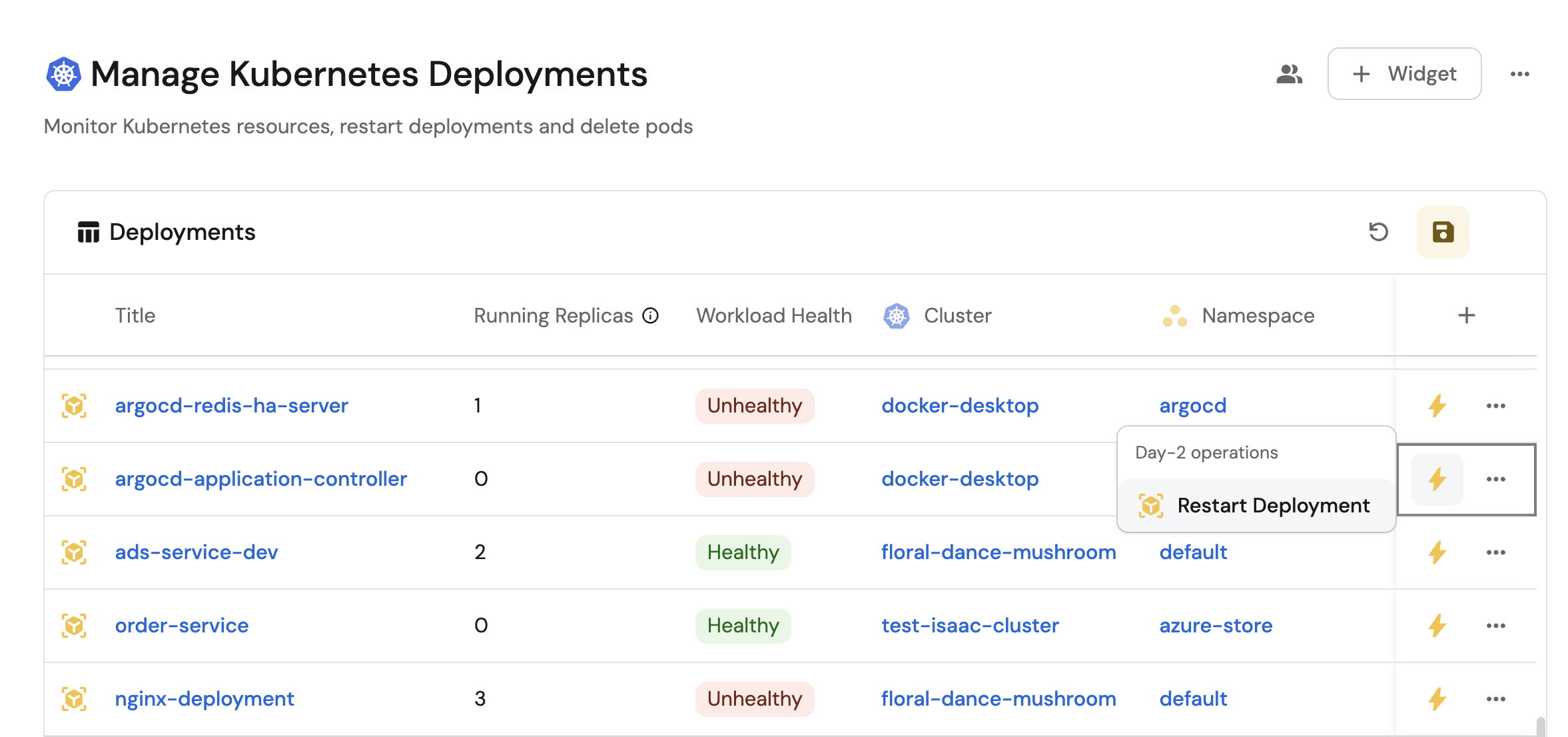
- Monitor the status and health of all Kubernetes deployments and pods across clusters from a single interface.
- Provide self-service capabilities for developers to restart deployments and manage pods.
Prerequisites
This guide assumes the following:
- You have a Port account and have completed the onboarding process.
- Port's Kubernetes integration is installed in your account.
We recommend creating a dedicated repository for the workflows that are used by Port actions.
Set up self-service actions
We will create self-service actions to manage your Kubernetes deployments and pods directly from Port using GitHub Actions. We will implement workflows to:
- Restart a Kubernetes deployment.
- Delete a Kubernetes pod.
To implement these use-cases, follow the steps below:
Add GitHub secrets
In your GitHub repository, go to Settings > Secrets and add the following secrets:
PORT_CLIENT_ID- Port Client ID learn more.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET- Port Client Secret learn more.
Configure Kubernetes authentication
Choose one of the following authentication methods based on your cluster setup:
- GKE
- EKS
- AKS
- Local (Kubeconfig)
This approach uses Google Cloud's authentication for GKE clusters.
-
Create a GCP service account in the Google Cloud Console:
- Go to IAM & Admin → Service Accounts.
- Click Create Service Account.
- Name it
github-actionsand add a description. - Grant the following roles:
- Kubernetes Engine Cluster Viewer (
roles/container.clusterViewer). - Kubernetes Engine Admin (
roles/container.admin).
- Kubernetes Engine Cluster Viewer (
-
Create a service account key:
- In the service account details, go to the Keys tab.
- Click Add Key → Create new key.
- Choose JSON format and download the key file.
-
Add to GitHub secrets:
GCP_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_KEY- The service account key JSON (minified to a single line).GCP_CLUSTER_LOCATION- The location of your cluster.
To avoid aggressive log sanitization, minify your service account JSON into a single line before storing it as a GitHub secret. You can use an online tool or the following command to minify the json:
jq -c '.' your-service-account-key.json | pbcopy
This approach uses AWS authentication for EKS clusters.
-
Create an IAM user in the AWS Console:
- Go to IAM → Users.
- Click Create user.
- Name it
github-actions-k8s. - Attach the AmazonEKSClusterPolicy managed policy.
-
Add the user to EKS Access Entries:
- Go to your EKS cluster console.
- Navigate to Access → IAM access entries.
- Click Create access entry.
- Select your IAM user and grant AmazonEKSAdminPolicy.
-
Create a cluster role binding for Kubernetes API access in your connected cluster:
Cluster role binding manifest (Click to expand)
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: github-actions-admin-binding
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: cluster-admin
subjects:
- kind: User
name: "arn:aws:iam::YOUR_ACCOUNT_ID:user/github-actions-k8s"
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io -
Create access keys for the IAM user:
- In the IAM user details, go to the Security credentials tab.
- Click Create access key.
- Choose Command Line Interface (CLI) and download the credentials.
-
Add to GitHub secrets:
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID- AWS access key ID.AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY- AWS secret access key.AWS_REGION- Your AWS region.
This approach uses Azure authentication for AKS clusters.
-
Create a service principal in the Azure Portal:
- Go to Azure Active Directory → App registrations.
- Click New registration.
- Name it
github-actions-aks. - Select Accounts in this organizational directory only.
- Click Register.
-
Create a client secret:
- In the app registration, go to Manage → Certificates & secrets.
- Click New client secret.
- Add a description and set expiration.
- Copy the secret value immediately (you won't be able to see it again).
-
Assign Azure roles to the service principal:
- Go to Subscriptions → Your subscription → Access control (IAM).
- Click Add → Add role assignment.
- Select
ContributororAzure Kubernetes Service Cluster User Rolerole. - Search for and select your service principal.
- Click Save.
-
Add to GitHub secrets:
AZURE_CLIENT_ID- Azure service principal client ID.AZURE_CLIENT_SECRET- Azure service principal client secret.AZURE_TENANT_ID- Azure tenant ID.AZURE_SUBSCRIPTION_ID- Azure subscription ID.AZURE_RESOURCE_GROUP- Azure resource group.
This approach uses a local kubeconfig file for authentication with a self-hosted runner.
This approach stores sensitive credentials in GitHub secrets and should only be used for testing or development environments.
Since GitHub's hosted runners cannot access localhost clusters, you'll need to set up a self-hosted runner on a machine that can access your local Kubernetes cluster. Follow the GitHub documentation to add a self-hosted runner to your repository.
-
Set up a self-hosted runner:
- Follow the GitHub documentation to add a self-hosted runner.
- Ensure the runner machine has access to your local Kubernetes cluster.
- Verify the runner is connected and ready in your repository settings.
-
Encode your kubeconfig:
cat ~/.kube/config | base64 | pbcopy
- Add to GitHub secrets:
KUBECONFIG- Your base64 encoded kubeconfig
Restart a Kubernetes deployment
Add GitHub workflow
Create the file .github/workflows/restart-k8s-deployment.yaml in the .github/workflows folder of your repository.
- GKE
- EKS
- AKS
- Local (Kubeconfig)
Restart GKE Deployment GitHub workflow (Click to expand)
name: Restart GKE Deployment
on:
workflow_dispatch:
inputs:
port_context:
required: true
description: 'Action and general context (blueprint, entity, run id, etc...)'
type: string
jobs:
restart-deployment:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: 'actions/checkout@v4'
- name: Inform Port of workflow start
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
runId: ${{fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId}}
logMessage: Configuring GCP credentials to restart GKE deployment ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.title }}
- id: 'auth'
uses: 'google-github-actions/auth@v2'
with:
credentials_json: '${{ secrets.GCP_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_KEY }}'
- id: 'get-credentials'
uses: 'google-github-actions/get-gke-credentials@v2'
with:
cluster_name: ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.properties.Cluster }}
location: '${{ secrets.GCP_CLUSTER_LOCATION }}'
- name: Restart Kubernetes deployment
run: |
kubectl rollout restart deployment/${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.identifier }} -n ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.relations.Namespace }}
- name: Wait for deployment rollout
run: |
kubectl rollout status deployment/${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.identifier }} -n ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.relations.Namespace }} --timeout=300s
- name: Inform Port about deployment restart success
if: success()
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
runId: ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId }}
status: 'SUCCESS'
logMessage: ✅ GKE deployment ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.title }} restarted successfully
summary: GKE deployment restart completed successfully
- name: Inform Port about deployment restart failure
if: failure()
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
runId: ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId }}
status: 'FAILURE'
logMessage: ❌ Failed to restart GKE deployment ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.title }}
summary: GKE deployment restart failed
Restart EKS Deployment GitHub workflow (Click to expand)
name: Restart EKS Deployment
on:
workflow_dispatch:
inputs:
port_context:
required: true
description: 'Action and general context (blueprint, entity, run id, etc...)'
type: string
jobs:
restart-deployment:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: 'actions/checkout@v4'
- name: Inform Port of workflow start
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
runId: ${{fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId}}
logMessage: Configuring AWS credentials to restart EKS deployment ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.title }}
- name: Configure AWS credentials
uses: aws-actions/configure-aws-credentials@v4
with:
aws-access-key-id: ${{ secrets.AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID }}
aws-secret-access-key: ${{ secrets.AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY }}
aws-region: ${{ secrets.AWS_REGION }}
- name: Update EKS Kubeconfig
run: aws eks --region ${{ secrets.AWS_REGION }} update-kubeconfig --name ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.properties.Cluster }}
- name: Restart Kubernetes deployment
run: |
kubectl rollout restart deployment/${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.identifier }} -n ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.relations.Namespace }}
- name: Wait for deployment rollout
run: |
kubectl rollout status deployment/${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.identifier }} -n ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.relations.Namespace }} --timeout=300s
- name: Inform Port about deployment restart success
if: success()
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
runId: ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId }}
status: 'SUCCESS'
logMessage: ✅ EKS deployment ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.title }} restarted successfully
summary: EKS deployment restart completed successfully
- name: Inform Port about deployment restart failure
if: failure()
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
runId: ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId }}
status: 'FAILURE'
logMessage: ❌ Failed to restart EKS deployment ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.title }}
summary: EKS deployment restart failed
Restart AKS Deployment GitHub workflow (Click to expand)
name: Restart AKS Deployment
on:
workflow_dispatch:
inputs:
port_context:
required: true
description: 'Action and general context (blueprint, entity, run id, etc...)'
type: string
jobs:
restart-deployment:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: 'actions/checkout@v4'
- name: Inform Port of workflow start
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
runId: ${{fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId}}
logMessage: Configuring Azure credentials to restart AKS deployment ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.title }}
- name: Azure Login
uses: azure/login@v2
with:
creds: '{"clientId":"${{ secrets.AZURE_CLIENT_ID }}","clientSecret":"${{ secrets.AZURE_CLIENT_SECRET }}","subscriptionId":"${{ secrets.AZURE_SUBSCRIPTION_ID }}","tenantId":"${{ secrets.AZURE_TENANT_ID }}"}'
- uses: azure/aks-set-context@v4
with:
resource-group: '${{ secrets.AZURE_RESOURCE_GROUP }}'
cluster-name: ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.properties.Cluster }}
- name: Restart Kubernetes deployment
run: |
kubectl rollout restart deployment/${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.identifier }} -n ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.relations.Namespace }}
- name: Wait for deployment rollout
run: |
kubectl rollout status deployment/${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.identifier }} -n ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.relations.Namespace }} --timeout=300s
- name: Inform Port about deployment restart success
if: success()
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
runId: ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId }}
status: 'SUCCESS'
logMessage: ✅ AKS deployment ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.title }} restarted successfully
summary: AKS deployment restart completed successfully
- name: Inform Port about deployment restart failure
if: failure()
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
runId: ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId }}
status: 'FAILURE'
logMessage: ❌ Failed to restart AKS deployment ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.title }}
summary: AKS deployment restart failed
Restart Local Deployment GitHub workflow (Click to expand)
name: Restart Local Deployment
on:
workflow_dispatch:
inputs:
port_context:
required: true
description: 'Action and general context (blueprint, entity, run id, etc...)'
type: string
jobs:
restart-deployment:
runs-on: self-hosted
steps:
- uses: 'actions/checkout@v4'
- name: Inform Port of workflow start
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
runId: ${{fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId}}
logMessage: Configuring local kubeconfig to restart deployment ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.title }}
- name: Configure kubectl
run: |
echo "${{ secrets.KUBECONFIG }}" | base64 -d > kubeconfig.yaml
export KUBECONFIG=kubeconfig.yaml
- name: Restart Kubernetes deployment
run: |
kubectl rollout restart deployment/${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.identifier }} -n ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.relations.Namespace }}
- name: Wait for deployment rollout
run: |
kubectl rollout status deployment/${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.identifier }} -n ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.relations.Namespace }} --timeout=300s
- name: Inform Port about deployment restart success
if: success()
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
runId: ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId }}
status: 'SUCCESS'
logMessage: ✅ Local deployment ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.title }} restarted successfully
summary: Local deployment restart completed successfully
- name: Inform Port about deployment restart failure
if: failure()
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
runId: ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId }}
status: 'FAILURE'
logMessage: ❌ Failed to restart local deployment ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.title }}
summary: Local deployment restart failed
Create Port action
-
Go to the Self-service page of your portal.
-
Click on the
+ New Actionbutton. -
Click on the
{...} Edit JSONbutton. -
Copy and paste the following JSON configuration into the editor.
Restart Kubernetes deployment action (Click to expand)
Modification RequiredMake sure to replace
<GITHUB_ORG>and<GITHUB_REPO>with your GitHub organization and repository names respectively.{
"identifier": "restart_k8s_deployment",
"title": "Restart Kubernetes Deployment",
"icon": "Cluster",
"description": "Restart a Kubernetes deployment to trigger a rolling update",
"trigger": {
"type": "self-service",
"operation": "DAY-2",
"userInputs": {
"properties": {},
"required": []
},
"blueprintIdentifier": "workload"
},
"invocationMethod": {
"type": "GITHUB",
"org": "<GITHUB-ORG>",
"repo": "<GITHUB-REPO>",
"workflow": "restart-k8s-deployment.yaml",
"workflowInputs": {
"port_context": {
"entity": "{{ .entity }}",
"runId": "{{ .run.id }}"
}
},
"reportWorkflowStatus": true
},
"requiredApproval": false
} -
Click
Save.
Now you should see the Restart Kubernetes Deployment action in the self-service page. 🎉
Delete a Kubernetes pod
Add GitHub workflow
Create the file .github/workflows/delete-k8s-pod.yaml in the .github/workflows folder of your repository.
- GKE
- EKS
- AKS
- Local (Kubeconfig)
Delete GKE Pod GitHub workflow (Click to expand)
name: Delete GKE Pod
on:
workflow_dispatch:
inputs:
port_context:
required: true
description: 'Action and general context (blueprint, entity, run id, etc...)'
type: string
jobs:
delete-pod:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: 'actions/checkout@v4'
- name: Inform Port of workflow start
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
runId: ${{fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId}}
logMessage: Configuring GCP credentials to delete GKE pod ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.title }}
- id: 'auth'
uses: 'google-github-actions/auth@v2'
with:
credentials_json: '${{ secrets.GCP_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_KEY }}'
- name: Set up Cloud SDK
uses: google-github-actions/setup-gcloud@v2
- id: 'get-credentials'
uses: 'google-github-actions/get-gke-credentials@v2'
with:
cluster_name: ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.properties.Cluster }}
location: '${{ secrets.GCP_CLUSTER_LOCATION }}'
- name: Delete Kubernetes pod
run: |
kubectl delete pod ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.identifier }} -n ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.properties.namespace }}
- name: Inform Port about pod deletion success
if: success()
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
runId: ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId }}
status: 'SUCCESS'
logMessage: ✅ GKE pod ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.title }} deleted successfully
summary: GKE pod deletion completed successfully
- name: Inform Port about pod deletion failure
if: failure()
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
runId: ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId }}
status: 'FAILURE'
logMessage: ❌ Failed to delete GKE pod ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.title }}
summary: GKE pod deletion failed
Delete EKS Pod GitHub workflow (Click to expand)
name: Delete EKS Pod
on:
workflow_dispatch:
inputs:
port_context:
required: true
description: 'Action and general context (blueprint, entity, run id, etc...)'
type: string
jobs:
delete-pod:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: 'actions/checkout@v4'
- name: Inform Port of workflow start
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
runId: ${{fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId}}
logMessage: Configuring AWS credentials to delete EKS pod ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.title }}
- name: Configure AWS credentials
uses: aws-actions/configure-aws-credentials@v4
with:
aws-access-key-id: ${{ secrets.AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID }}
aws-secret-access-key: ${{ secrets.AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY }}
aws-region: ${{ secrets.AWS_REGION }}
- name: Update EKS Kubeconfig
run: aws eks --region ${{ secrets.AWS_REGION }} update-kubeconfig --name ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.properties.cluster }}
- name: Delete Kubernetes pod
run: |
kubectl delete pod ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.identifier }} -n ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.properties.namespace }}
- name: Inform Port about pod deletion success
if: success()
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
runId: ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId }}
status: 'SUCCESS'
logMessage: ✅ EKS pod ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.title }} deleted successfully
summary: EKS pod deletion completed successfully
- name: Inform Port about pod deletion failure
if: failure()
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
runId: ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId }}
status: 'FAILURE'
logMessage: ❌ Failed to delete EKS pod ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.title }}
summary: EKS pod deletion failed
Delete AKS Pod GitHub workflow (Click to expand)
name: Delete AKS Pod
on:
workflow_dispatch:
inputs:
port_context:
required: true
description: 'Action and general context (blueprint, entity, run id, etc...)'
type: string
jobs:
delete-pod:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: 'actions/checkout@v4'
- name: Inform Port of workflow start
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
runId: ${{fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId}}
logMessage: Configuring Azure credentials to delete AKS pod ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.title }}
- name: Azure Login
uses: azure/login@v2
with:
creds: '{"clientId":"${{ secrets.AZURE_CLIENT_ID }}","clientSecret":"${{ secrets.AZURE_CLIENT_SECRET }}","subscriptionId":"${{ secrets.AZURE_SUBSCRIPTION_ID }}","tenantId":"${{ secrets.AZURE_TENANT_ID }}"}'
- uses: azure/aks-set-context@v4
with:
resource-group: '${{ secrets.AZURE_RESOURCE_GROUP }}'
cluster-name: ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.properties.cluster }}
- name: Delete Kubernetes pod
run: |
kubectl delete pod ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.identifier }} -n ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.properties.namespace }}
- name: Inform Port about pod deletion success
if: success()
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
runId: ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId }}
status: 'SUCCESS'
logMessage: ✅ AKS pod ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.title }} deleted successfully
summary: AKS pod deletion completed successfully
- name: Inform Port about pod deletion failure
if: failure()
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
runId: ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId }}
status: 'FAILURE'
logMessage: ❌ Failed to delete AKS pod ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.title }}
summary: AKS pod deletion failed
Delete Local Pod GitHub workflow (Click to expand)
name: Delete Local Pod
on:
workflow_dispatch:
inputs:
port_context:
required: true
description: 'Action and general context (blueprint, entity, run id, etc...)'
type: string
jobs:
delete-pod:
runs-on: self-hosted
steps:
- uses: 'actions/checkout@v4'
- name: Inform Port of workflow start
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
runId: ${{fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId}}
logMessage: Configuring local kubeconfig to delete pod ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.title }}
- name: Configure kubectl
run: |
echo "${{ secrets.KUBECONFIG }}" | base64 -d > kubeconfig.yaml
export KUBECONFIG=kubeconfig.yaml
- name: Delete Kubernetes pod
run: |
kubectl delete pod ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.identifier }} -n ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.properties.namespace }}
- name: Inform Port about pod deletion success
if: success()
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
runId: ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId }}
status: 'SUCCESS'
logMessage: ✅ Local pod ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.title }} deleted successfully
summary: Local pod deletion completed successfully
- name: Inform Port about pod deletion failure
if: failure()
uses: port-labs/port-github-action@v1
with:
clientId: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_ID }}
clientSecret: ${{ secrets.PORT_CLIENT_SECRET }}
baseUrl: https://api.getport.io
operation: PATCH_RUN
runId: ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).runId }}
status: 'FAILURE'
logMessage: ❌ Failed to delete local pod ${{ fromJson(inputs.port_context).entity.title }}
summary: Local pod deletion failed
Create Port action
-
Go to the Self-service page of your portal.
-
Click on the
+ New Actionbutton. -
Click on the
{...} Edit JSONbutton. -
Copy and paste the following JSON configuration into the editor.
Delete Kubernetes pod action (Click to expand)
Modification RequiredMake sure to replace
<GITHUB_ORG>and<GITHUB_REPO>with your GitHub organization and repository names respectively.{
"identifier": "delete_k8s_pod",
"title": "Delete Kubernetes Pod",
"icon": "Cluster",
"description": "Delete a Kubernetes pod (will be recreated by the deployment)",
"trigger": {
"type": "self-service",
"operation": "DELETE",
"userInputs": {
"properties": {},
"required": []
},
"blueprintIdentifier": "pod"
},
"invocationMethod": {
"type": "GITHUB",
"org": "<GITHUB-ORG>",
"repo": "<GITHUB-REPO>",
"workflow": "delete-k8s-pod.yaml",
"workflowInputs": {
"port_context": {
"entity": "{{ .entity }}",
"runId": "{{ .run.id }}"
}
},
"reportWorkflowStatus": true
},
"requiredApproval": false
} -
Click
Save.
Now you should see the Delete Kubernetes Pod action in the self-service page. 🎉